Are you looking for ways to fix your sleep schedule?
You may be working as a firefighter, police officer, paramedic, or nurse, and your job requires you to be on rotating shifts, or on call to respond to emergencies at any time.
Or it could be that your lifestyle forces you to keep late hours, without a lot of rest.
If any of these descriptions fit you, then you are part of the 40% of all adult Americans who are sleep deprived. Our modern, Western environment is interfering with our natural sleeping patterns. People sleep less now than they did in the past, and there has also been a large decline in sleep quality.
Sleep deprivation happens when a person does not get to sleep the number of hours that is recommended by the National Sleep Foundation for their age.
Today, we’ll give you tried-and-proven strategies for fixing your sleep schedule to combat the effects of sleep deprivation. We’ll also discuss the importance of getting the recommended number of slumber hours for your physical and mental health, as well as for your general well-being.
The Importance of a Stable Sleep Schedule
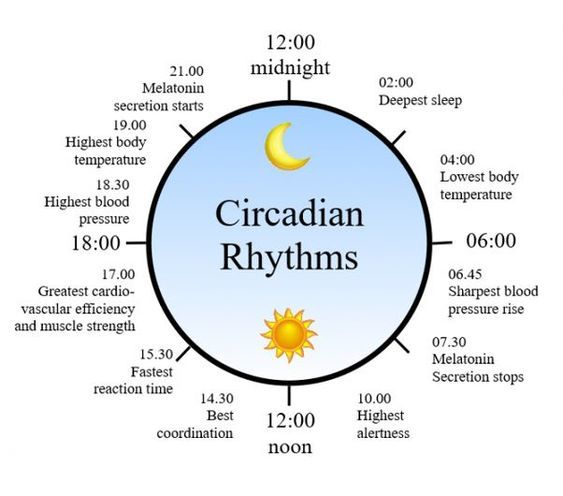
The health benefits of consistently getting a sufficient amount of sleep go beyond just feeling rested while you are awake. The infographic below helps us understand how our body clocks work.
This internal clock works on a 24-hour schedule, managing sleeping and waking times, along with the biological processes that happen in the body while it is at rest.
When we are in sync with our body clocks, we are in our optimal health (when we wake and sleep according to the natural cycle). Problems arise when we go against the natural rhythm of our bodies because of our jobs, social lives, or illness.
For some people, being sleep deprived is unavoidable in their line of work. They either work the night shift or have rotating shift schedules. However, getting way less than the recommended hours of sleep time can take a toll on one’s health, with possibly fatal results.
Being sleep deprived for even just one night weakens the immune system, making you vulnerable to illnesses. This means that are you more susceptible to becoming ill, and it can also take your body a longer time to recover from an illness that it is unable to fight off efficiently. This poses potential damage to your brain.
There is also a strong correlation between lack of sleep and a higher risk for respiratory diseases. Ventilation and respiration both change while you are sleeping.
Specifically, your breathing becomes faster and more inconsistent during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep. Recently there is an increase in the recognition of a dual interaction between sleep deprivation and chronic lung disease.
Furthermore, a constant lack of sleep contributes to weight gain. In one review of many sleep studies, both children and adults who did not get enough sleep were 89% and 55% (respectively) more likely to gain weight to the point of becoming obese.
A lack of sleep also contributes to a higher risk of developing diabetes, having heart disease, and having poor or unhealthy hormone production. Sleep deprivation is often a factor in tragic accidents that involve vehicles (trains, cars, and airplanes).
The four-minute animated video below shows us the fatal effects of sleep deprivation. Losing sleep can cause bodily harm and even death. Real-life examples of people experiencing the effects of lack of sleep are included in the video. The video also explains the physiological mechanism of sleep.
What Are the Benefits of Good Sleep?
Strengthens your immunity
As opposed to being sleep deprived, good sleep boosts your immune system and your body’s capability to fight off diseases. Researchers know that there is a complex relationship between your sleep-wake cycle and your immune system.
Components of your immune system influence your quantity and quality of sleep, and the sleep you get has a direct effect on your immunity. In fact, even losing just a little bit of sleep can have a significant impact on how your immune system functions.
One reason that sleep impacts your immunity so much is that certain disease-fighting compounds are created or released during sleep. Your body needs these unique hormones and proteins to fight off diseases and infections.
When you don't get enough sleep, you decrease the amount of these substances in your body, making you more vulnerable to every virus and bacteria you encounter.
This can also impede your body from recovering quickly if you are already sick because your body won't have what it needs to fight whatever is making you sick.
Improves your focus and productivity
A well-rested brain can function better, leading to a rise in ability to concentrate, and in your overall productivity. However, when you're sleep deprived, your focus drifts, making it harder to absorb information.
Without enough sleep, over-worked neurons can't function and you are unable to access information that you learned previously. You also lose your ability to make proper decisions because your judgment becomes impaired. This means that you are less likely to perform well.
Prevents accidents
You are able to focus on what is going on around you when you are well rested. Alternatively, research shows that people who are not well rested often are unable to pick up on relevant cues.

Lapses in focus due to a lack of sleep may result in accidents or injuries. In fact, when a person accumulates 22 hours of sleep deprivation, it impairs their neurobehavioral performance to the point that it is comparable to a 0.08 percent blood alcohol content, which is considered to be legally drunk in the United States.
One study on student interns showed that interns who worked a traditional schedule with extended working hours of over 24 hours made 36% more serious medical errors than those who were on a schedule that allowed them to get more sleep.
Keeps your weight down
Your metabolic cycle is more in sync with the patterns of the circadian rhythm when you sleep well. When you don't get enough sleep, your cortisol levels rise, which signals your body to hold onto your calories to fuel your waking hours.
Research has shown that when people who were dieting reduced the amount of sleep they got over a two-week period, the amount of fat they lost decreased by 55%, despite the fact that their calorie consumption remained unchanged.
Those who were sleep deprived felt hungrier and less satiated after meals, and they had reduced energy.
Also, studies show that people who are starved of sleep often turn to late-night snacking, and typically choose high-carb snacks. Sleeping too little may also prompt people to eat larger portions of food, increasing weight gain.
Lowers your stress levels
The lack of sleep contributes to elevated levels of cortisol (stress-producing hormones), and you can lower this by getting some quality shut-eye. Sleeping in time with your body’s circadian rhythm and getting the amount of sleep that you need can help you naturally lower your cortisol levels.
If you are able to go to sleep at about 10:00 pm, it will help you avoid a late-night spike in cortisol, which could make it difficult for you to fall asleep. Going to sleep at this time also takes advantage of your body's natural melatonin production, which begins around sunset each night to help you calm down.
How to Fix Your Sleep Schedule
You are probably wondering what are some things that you can do to fix this issue if your working schedule is not conducive to getting a typical night's sleep.
Here are some tried-and-tested strategies to fix your sleep schedule and cope with rotating shifts that may be required in your job.
1. Be strict with yourself when it comes to bedtime.
Your body craves consistency. When you have a routine, your body systems learn to anticipate events and prepare for them.
For example, your digestive system activates before your typical meal times so your body can process food with more efficiency. Similarly, when you’ve established a workable bedtime, your body will start to calm down when that time is approaching.
Stick to your schedule. Having a predictable sleeping schedule is the key to success. If you go to bed at the same time every day, you will start waking up at the same time as well without having to use an alarm clock.
Remember to also be devoted to your bedtime as much as you can on the weekends to keep your sleep schedule as routine as possible.
2. Avoid caffeine, alcohol, or nicotine.
Once you’ve set your sleep schedule, avoid smoking or drinking caffeinated or alcoholic beverages close to that time or at the end of your shift. These stimulants can cause a delay in your sleep.

Caffeine and nicotine are stimulants that will keep you from falling into the deep, restorative sleep that your body needs. When you consume caffeine or nicotine within three hours of trying to go to sleep, it can make it hard to go to sleep until the effects wear off.
While most people know that drinks like soda, tea, and coffee have caffeine in them, some people might not realize that foods like chocolate contain caffeine as well.
While alcohol may initially make you feel sleepy, it can have the opposite effect in the middle of the night, causing you to wake up and not be able to get back to sleep.
3. Use blinds or curtains that block out sunlight.
Light has a huge impact on sleep. The absence of light at night sends the vital message to your body that it is time to sleep. When you are exposed to light first thing in the morning, it stimulates your mind and body to wake up and get energized.
Having exposure to light at night also increases your alertness, which can pose a serious issue for restorative sleep. If you have any light in your room at night, it can lead to frequent wake-ups in the middle of the night where you may have trouble falling back asleep.
If you work at night, sunlight can be your enemy when you are trying to catch up on your sleep. Sunlight naturally stimulates the circadian rhythm, but it can be disadvantageous for you if you’re trying to sleep during the day after a night shift.
Use heavy curtains or blackout blinds to block light while you sleep. Also, make sure to limit your screen time in the hours leading up to going to sleep.
For more tips on how to start off your morning right, watch the video below for the 7 step process you can use to create a routine that works for you.
4. Avoid sleeping in during your day off.
Again, predictability helps you regain a stable sleep schedule. As much as you can, stick to a regular schedule for sleeping and waking, even when it’s your day off.
You can't “bank” sleep or “catch up” on lost sleep. You need to try to remain in the same sleeping routine every night, regardless of what you have going on during the day.
5. Avoid working out or eating close to your bedtime.
Exercise gets your heart rate pumping and your endorphins flowing. This means that your body is more alert. It takes a while after exercising for your body to calm down, even if you feel like you did a hard workout and should be exhausted.
Also, eating too close to your bedtime can disturb your sleep because it stimulates your stomach acids, and when you lie down those acids can rise up into your throat.
This heartburn can cause discomfort that keeps you awake. If you really need a late-night snack, eat a bowl of cereal or cheese and crackers. These mineral-rich foods (i.e., tryptophan and calcium) help promote sleep.
6. Do not delay your intended bedtime.
Sometimes, even if you try to get to bed early, your thoughts start to crowd your head the moment you hit the pillow.
If you had a long or busy day, you may start to recount the events, or think about the things you need to do the next day. However, it is important to do your best to not lie awake in bed allowing your thoughts to keep you from falling asleep.
It can help if you have a calming routine that you do every night to remind your body that it is time to get ready to go to sleep. This may involve taking a warm bath or doing some light reading.
You can also use the 12-minute guided meditation video below to achieve a deep state of relaxation to facilitate better sleep. It helps you let go of worrying thoughts and encourages you to focus on three wonderful things that you experienced during the day.
7. Aim to sleep for seven to nine hours.
To fully recover from a sleep deficit, you need to sleep from seven to nine hours. Make this your goal after every night shift. In fact, research has shown that these are the magic numbers to help improve longevity.
Studies have shown that people who generally sleep for under five to seven hours each night are 12% more likely to suffer from premature death. Interestingly, people who sleep more than nine hours each night have a higher risk of premature death—30%.
Studies have also found that those who reduce the amount of sleep they get each night from seven or eight hours to under seven hours are at a higher risk of death from all causes. Researchers also found an increased risk of death from all causes in people who slept for a long time every night.
8. Ask for support from your family.
Let your family know about your work and sleep hours, and ask for their support in screening phone calls and visitors to prevent disruption while you sleep.
Being disrupted involuntarily while you are sleeping may bring you out of a deep sleep and alter your sleep-wake pattern for the duration of your sleep.
Before waking up naturally, your body will move into a rapid eye movement (REM) state, which is a lighter state of sleep than the non-rapid eye movement (NREM) state.
Skipping this transition and suddenly going from NREM sleep to being awake can lead to more grogginess for the remainder of the day, even if you go back to sleep.
Set guidelines with your family to make it clear if there are some phone calls that are emergencies and others that can wait to be handled until you're awake. You may also want to let your friends know so they won't try to call you during your sleeping hours.
9. Avoid long commutes after your shift.
Although avoiding long commutes after work may still be recommended no matter what time you get off work, it’s definitely a good idea to avoid a long commute if you have to work a night shift.

Try to find a place to sleep that is in close proximity to your work if your home is far away.
This way, you don't have to force yourself to stay awake while being exposed to light when it is time for you to get some rest. Long commutes take away precious time for a good sleep.
10. Try to not work night shifts for extended periods of time.
If you can, limit the number of times you work night shifts to avoid being increasingly deprived of sleep every night.
Even if you are only working for four night shifts in a row, it can make it harder for you to recuperate and get the amount of sleep that your body needs. If possible, work only a few night shifts during your work week.
Also, make sure that you schedule either a “normal” nine-to-five shift or a day off during the days that fall in between night shifts so you aren't doing a series of shifts without a break. You’ll be surprised at how quickly you can recover when you plan your work schedule around your sleep schedule.
11. Make sure to sleep in an ideal environment.
The ideal sleep environment helps you fall asleep faster and provides comfort during your slumber. This is a huge part of sleep hygiene, which is the recommended practices that are intended to promote a better quality of sleep.
Aside from having a dark environment to sleep in that is free from noise and distractions, you also want to make sure that it is slightly cool in the room and there are no electronics running around you.
You may have to create this environment by getting blackout curtains, putting a fan in the room, or getting a white noise machine. However, anything you can do to make the environment calming to you is what is best.
Final Thoughts on How to Fix Your Sleep Schedule
Fixing your sleep schedule to combat the effects of sleep deprivation after night shifts can be effective if you set a predictable routine that you’ll commit to following to the letter.
Hopefully, the strategies above on how to fix your sleep schedule can give you good sleep every time. Take the steps gradually, and don’t be so hard on yourself if you don’t see the results immediately.
If you find yourself having sleep difficulties that cannot be improved by the techniques suggested above, you might want to consult a health care professional or a specialist for proper identification of underlying conditions. A medical specialist would also be able to provide a course of treatment when necessary.
Having good sleep hygiene is necessary for optimal health. If you are interested in learning more about good habits, read the following articles:
- 53 Simple Healthy Habits to Improve Your Quality of Life
- 17 Healthy Ways to Fall Asleep Earlier
- 23 Evening Routine Habits and Ideas to Perfectly End Your Day